Fully Explain the Difference Between Consumer Goods and Capital Goods
Complete each of the following tasks with short paragraphs. Fully explain the difference between the following USE EXAMPLES FOR EACH.
In other words things that we grow or make and try to sell to buyers.
. Capital goods are bought by companies desirous of making the consumer goods. Consumer goods are those products that are only using for consumers whereas capital goods are those products that are applying for one business to enhance another business. One buys consumer goods from retail stores for personal family or household use.
Consumption goods are regarded as those goods that are most suited for final consumption. Explain the relationship between scarcity choices and trade-offs ____5 B. It just depends on how it will be occupied.
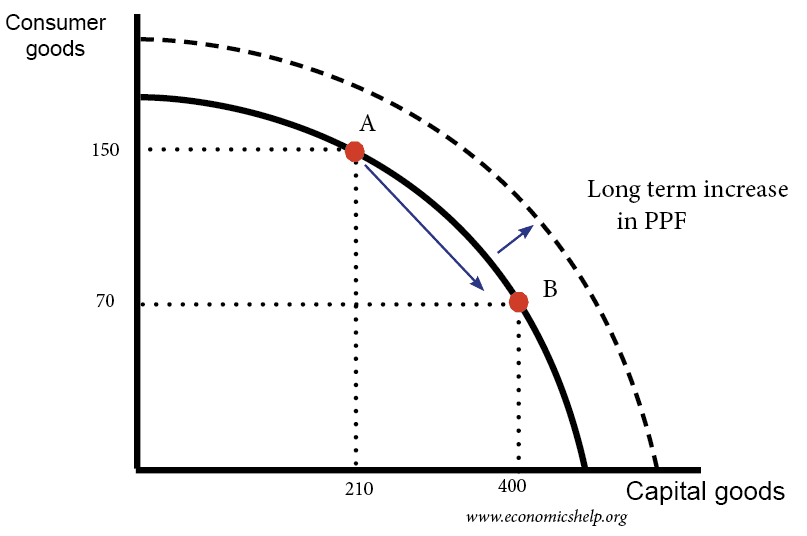
Fully explain three specific situations that would shift PPF-B outward. Consumer Goods vs Industrial Goods. Capital goods are goods used to make more consumer goods whereas consumer goods are goods meant for the use of end consumers only.
Explain the difference between a change in demand and change in quantity demand. Consumption goods are those goods which are used by consumer for personal use and they are ready for use as they are. Fully explain three specific situations that would shift PPF-B outward.
Capital goods are not readily convertible into cash. Capital goods are goods used by businesses to produce goods and services used by consumers. While capital goods are those goods for the production of other goods in other words they are final goods yet they are not final goods to be ultimately consumed.
Trade offs and Opportunity Cost ____3 ii. The difference again lies in its utilization. A capital good is any good deployed to help increase future production.
In other words the end user of consumer goods is the consumer itself while the capital goods are those goods that are used for production of consumption goods. Capital goods are things that businesses buy to make other things. Define scarcity and explain how it is related to choices and trade-offs ____3 B.
Normative and Positive Economics ____3. Business natural resources not modified by. These type of goods last a long time ie they are durable.
1cii Fully explain the difference between normative and positive economics. Capital goods are referred to as the fixed or tangible assets that are purchased by a business in order to produce finished products or consumer goods. Physical products or goods have been classified into two separate categories consumer goods and industrial goods.
Up to 24 cash back Fully explain the difference between the following USE EXAMPLES. Explain the relationship between scarcity choices and trade-offs ____5 B. They are different than financial capitalwhich refers to funds companies use to grow their.
Up to 24 cash back Consumer Goods and Capital Goods ____3 ii. Price costs and opportunity cost ____4 C. An apple bought at a grocery store and immediately eaten is a consumer good.
Complete each of the following tasks with short paragraphs. The number of buyers is large. Explain the difference between a change in demand and change in quantity demand.
In other words consumption goods can be used few times while capital goods can. But the more the capital goods are produced now more will be the productive capacity of the economy in future. Consumer Goods vs Capital Goods.
One example of capital goods is the coffee machine. Consumer Goods and Capital Goods ____3 ii. Consumer Goods and Capital Goods ____3 ii.
Consumer goods are not using for upcoming business or productivity while capital goods are using for the next activity or harvesting for consumer goods. Draw and label these changes on three separate graphs. Price costs and opportunity cost ____4 C.
Industrial goods have only limited number of buyers. The most common capital goods are property plant and equipment or PPE. Human hands are not considered capital goodsalthough both are factors of production.
Clearly there is a trade-off between consumer goods and capital goods. Now let us look at a few points of difference between consumption goods and final goods. Fully explain the difference between the following USE EXAMPLES.
Capital goods are also called as intermediate goodsdurable goods or economic capital. They are durable and they do not wear out quickly. Fully explain three specific situations that would shift PPF-B outward.
Capital goods are usually considered fixed. Consumer Goods and Capital Goods ____3 v. The same physical good could be a consumer good or a capital good.
Differentiate between the following terms. Draw and label these changes on three separate graphs. Consumer Goods and Capital Goods ____3 Normative and Positive Economics ____3 Allocative and Productive Efficiency _____3.
Differentiate between the following terms. Normative and Positive Economics ____3 iv. The demand for consumer goods is a direct demand.
The demand for industrial goods is a derived demand. It is derived from the demand for consumer goods which are made using the industrial goods. If an economy produces more of capital goods it is producing less of consumer goods.
They are goods used by consumers and have no future productive use. Price and Cost ____3 iii. Draw and label these changes.
We exchange money for example for goods and services. Consumer goods are any goods that are not capital goods. The classification or distinction between these two types of goods is necessary in order to determine different efficient strategies which are required to help in moving the products through the marketing.
In return a larger volume of consumer goods can be produced in future. Capital goods are indirectly consumed because they are goods used to make or produce the consumer godds. The main difference between Consumer Goods and Capital Goods is that consumer goods are the goods that are used by consumers and do not have any future productive use while capital goods are the goods that are used by one business to create products that can be used by another business to create consumer goods.
Up to 24 cash back Consumer Goods and Capital Goods ____3 Normative and Positive Economics ____3. An identical apple bought by a company to beat a hasty retreat apple juice is a capital good. Fully explain the difference between the following USE EXAMPLES.


No comments for "Fully Explain the Difference Between Consumer Goods and Capital Goods"
Post a Comment